Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, is a method of obtaining images from inside the body through the use of high-frequency sound waves. The reflected sound wave echoes are recorded and displayed as real-time visual images. No radiation is involved in ultrasound imaging.
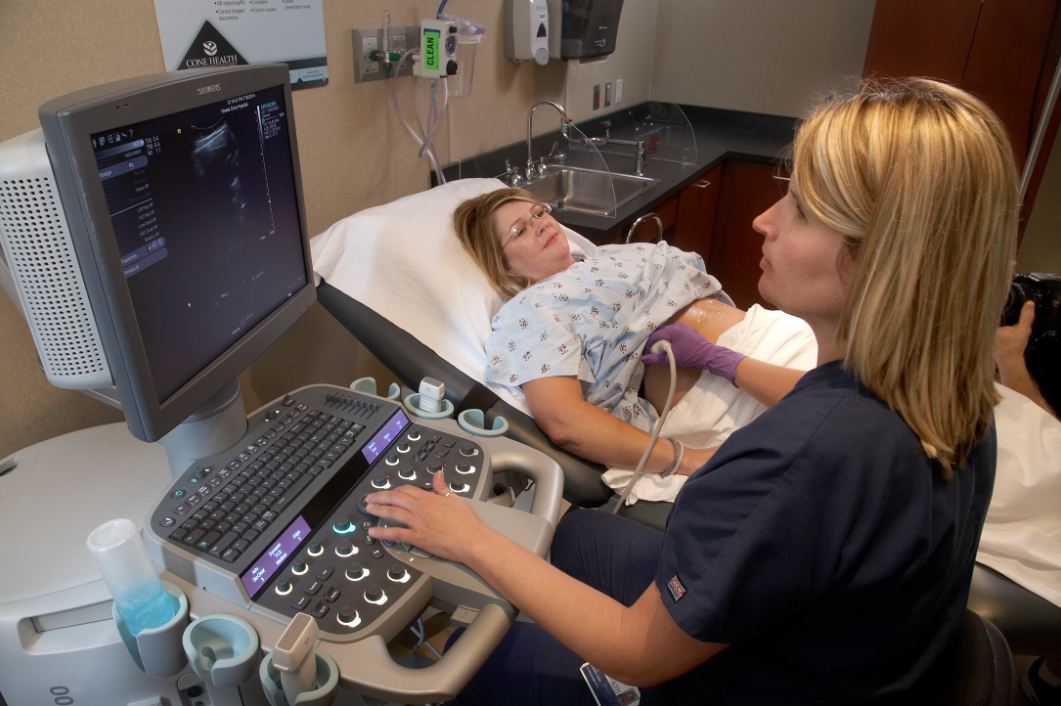
A Greensboro Radiology Sonographer performs an ultrasound on a patient.
Ultrasound is a useful way to examine many of the body's internal organs, including but not limited to the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, uterus, ovaries, aorta and other major blood vessels. Its ability to evaluate soft tissues may be complementary to other modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT). Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show movement of internal tissues and organs. This enables the physician to see certain processes occurring in the body in order to diagnose some conditions.
Ultrasound has difficulty penetrating bone and gas, and therefore cannot image within or through these substances. For visualization of bone or gas-containing organs such as lung or bowel, other imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) may be selected.